Chapter 2 - Data and Data Processing
Chapter 2 Part 1 Concepts of data, information and knowledge
Part 1: Concepts of data, information and knowledge
Structure of the knowledge pyramid
The concept of data
The term data refers to information or values that are available in a raw or processed form and serve as the basis for decisions, calculations or analyses. It can take the form of numbers, text, images, audio files or other formats and represents the building blocks of knowledge when placed in context.
Characteristics of data
- Neutrality: Data is initially neutral information without interpretation or context.
- Example: "25" is a data value that has no meaning without context.
- Formats: Data can be available in various forms, e.g. as numbers, letters, symbols, images, videos or sounds.
- Use: Data is the basis for analyses, calculations, reports and decisions.
- Storage: Data can be stored digitally (e.g. in databases, files) or analog (e.g. on paper).
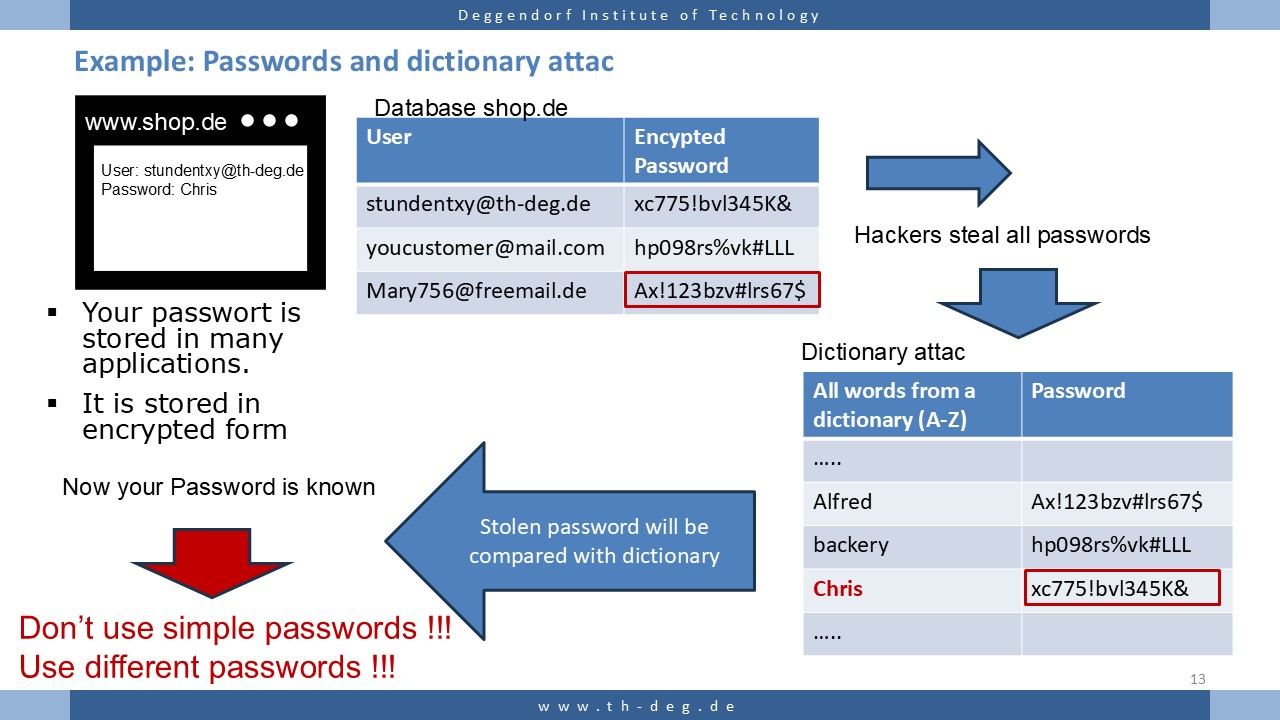
- Data can be divided into different categories. These classifications help to better understand, organize and use data in a targeted manner.
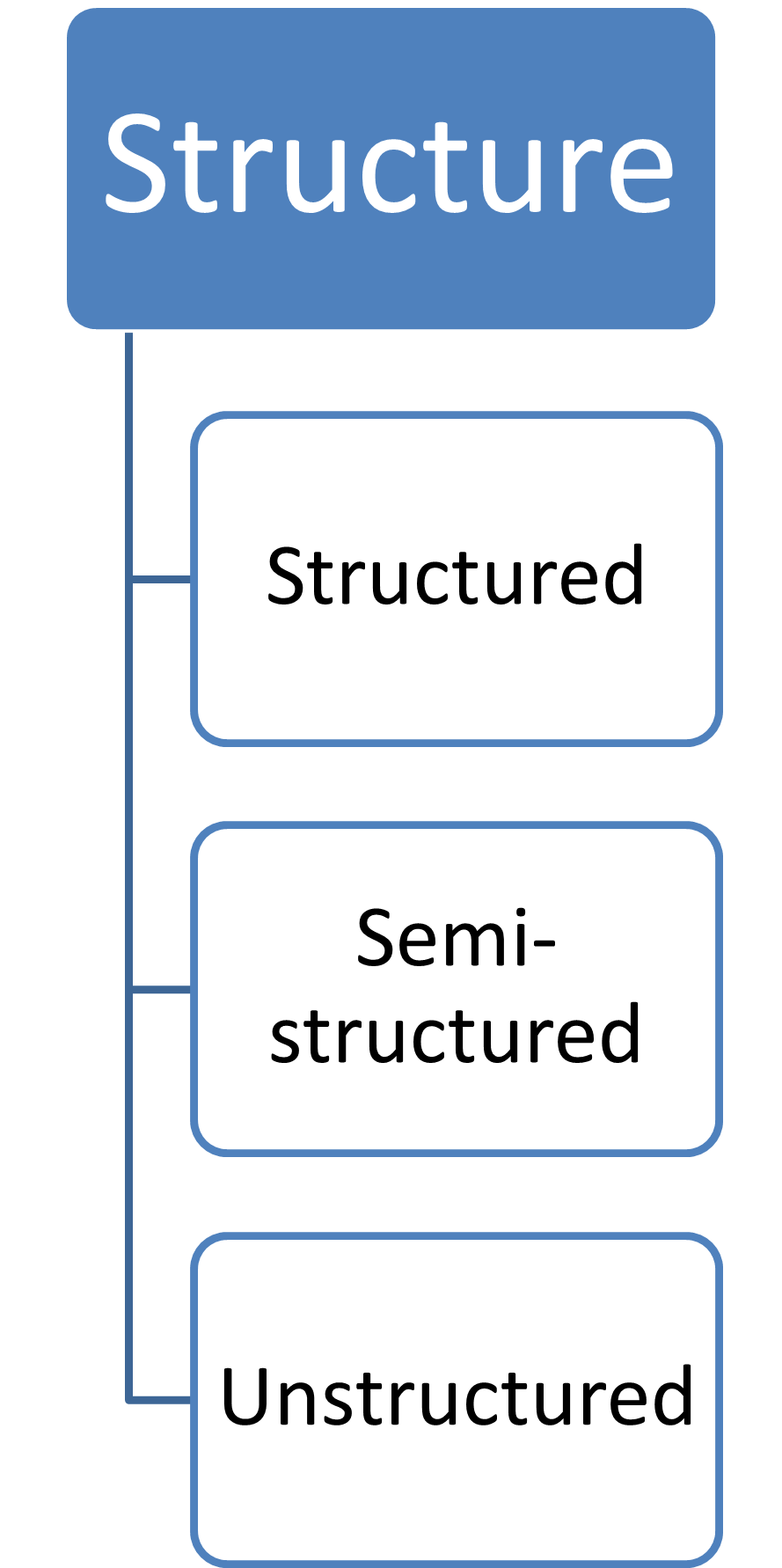
Data classification
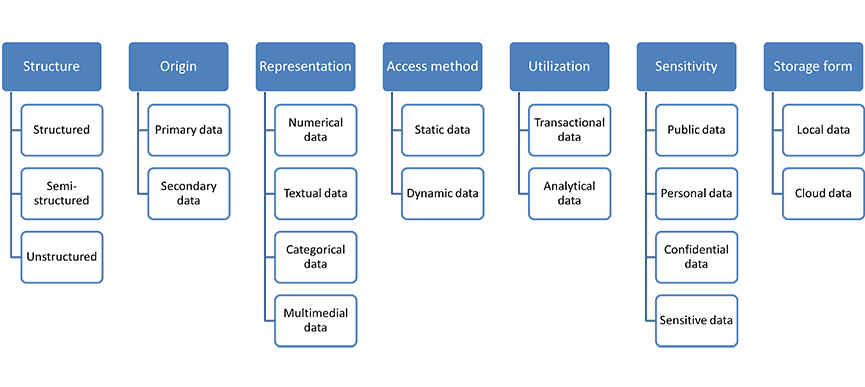
By structure
 |
Structured data
Unstructured data
Semi-structured data
|
By origin
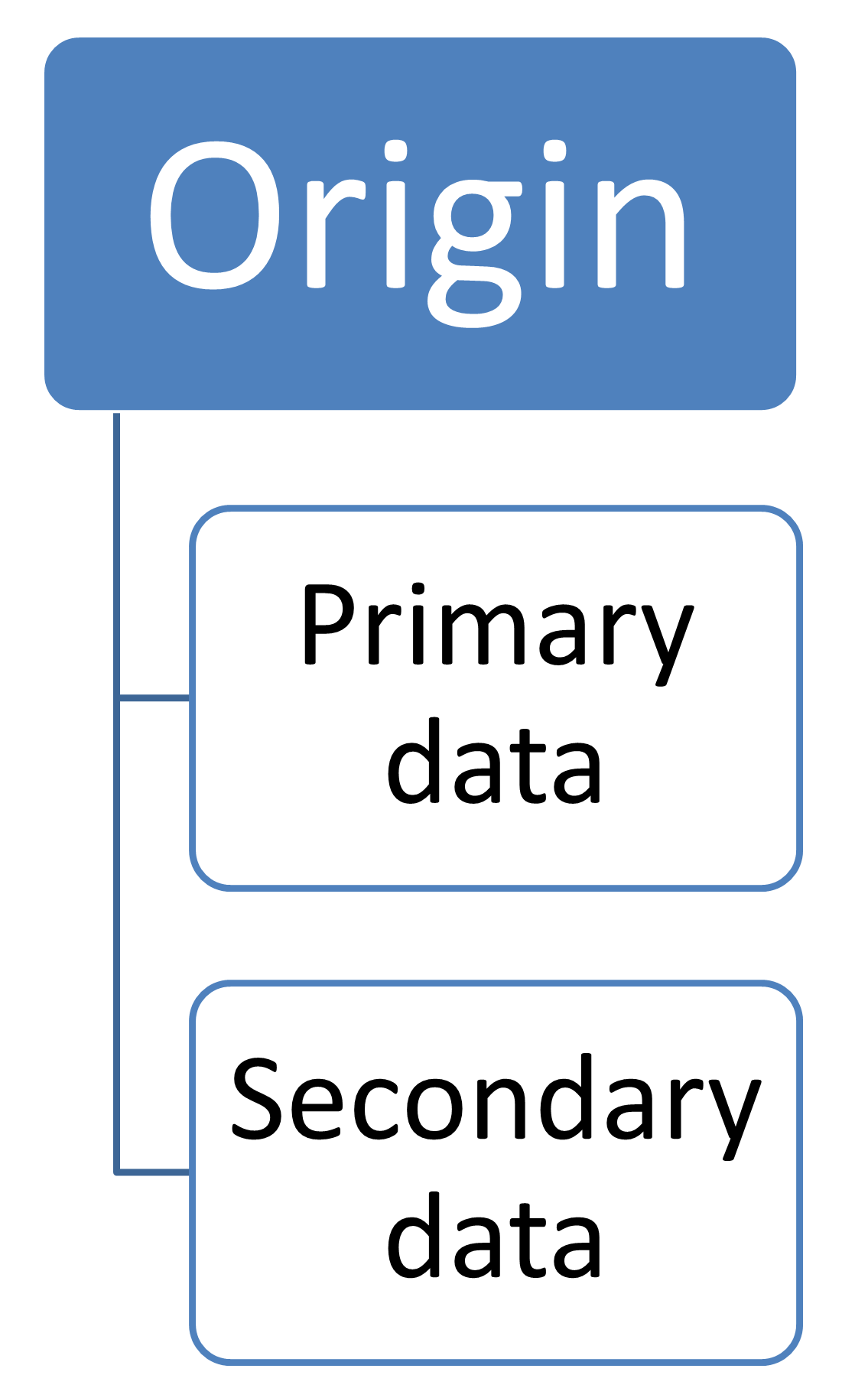 |
Primary data
Secondary data
|
By representation
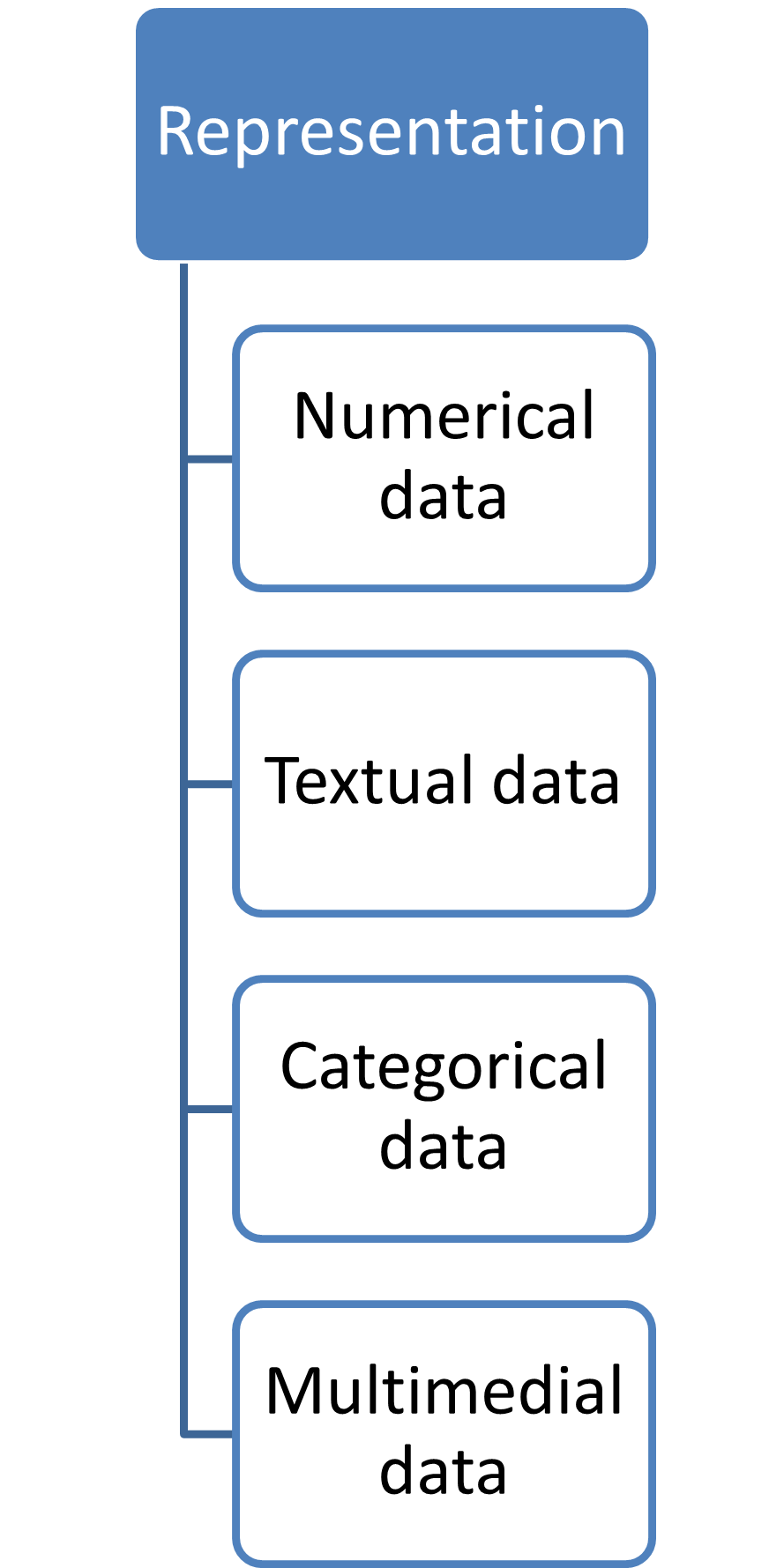 |
Numerical data
Categorical data
|
Textual data
Multimedia data
|
By access method
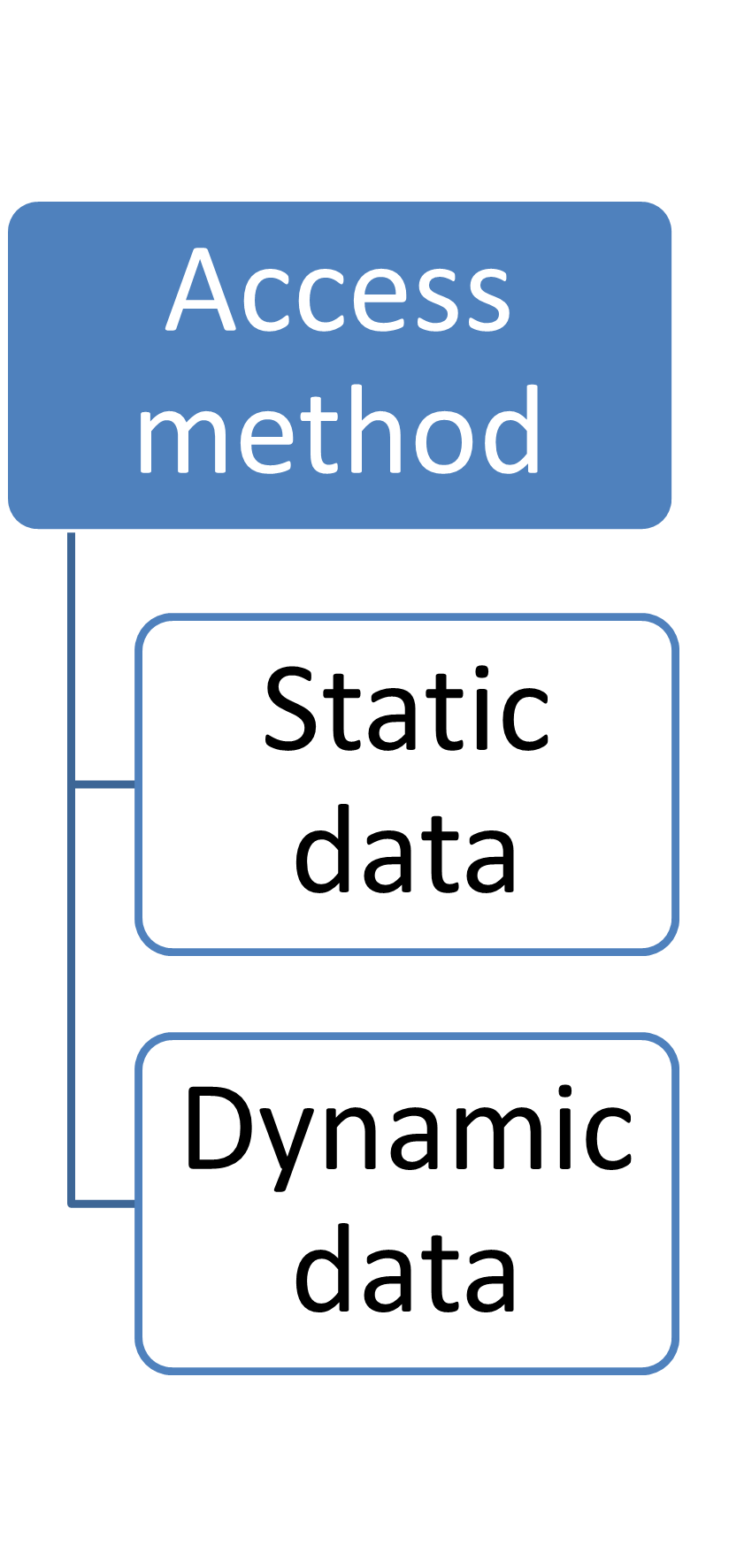 |
Static data
Dynamic data
|
After use
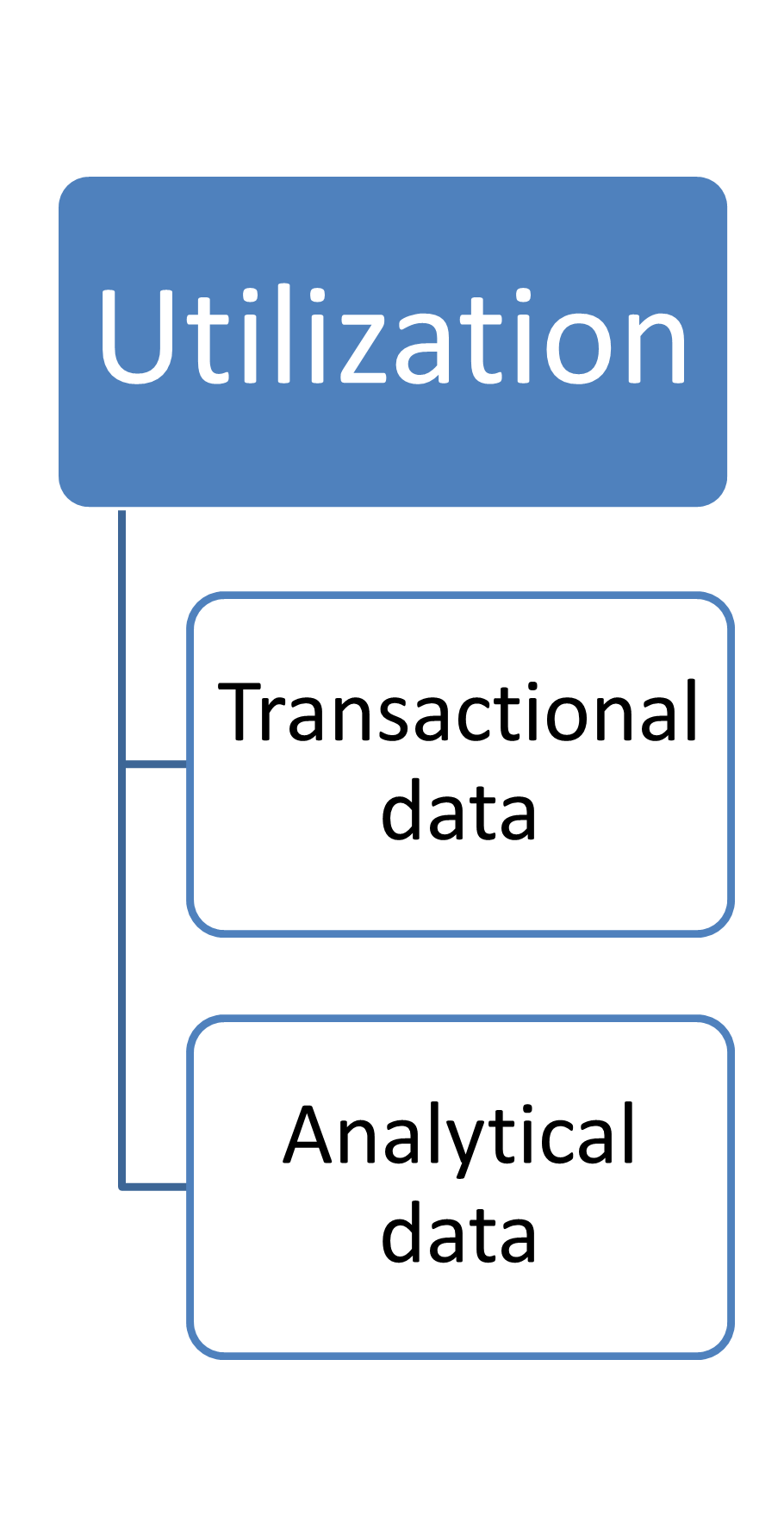 |
Transactional data
Analytical data
|
By sensitivity
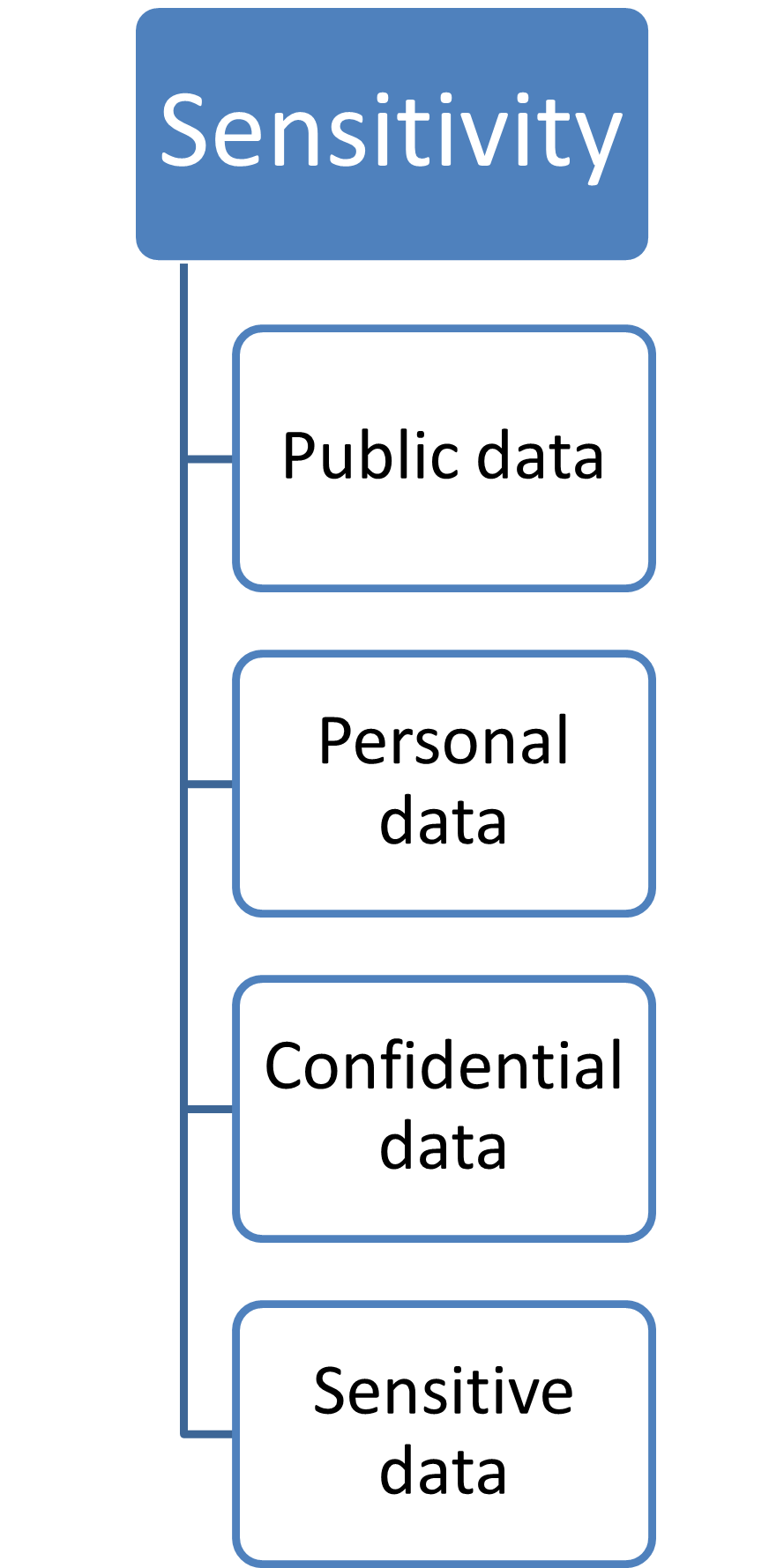 |
Public data
Confidential data
|
Personal data
Sensitive data
|
By storage form
 |
Local data
Cloud data
|