Unit 2: Functional Diagnostics and Imaging Techniques
g. Functional diagnostics
1. Spirometry:
According to the United Kingdom's National Health System (NHS), spirometry is a simple test used to help diagnose and monitor certain lung conditions by measuring how much air a person can breathe out in one forced breath. It's carried out using a device called a spirometer, which is a small machine attached by a cable to a mouthpiece.
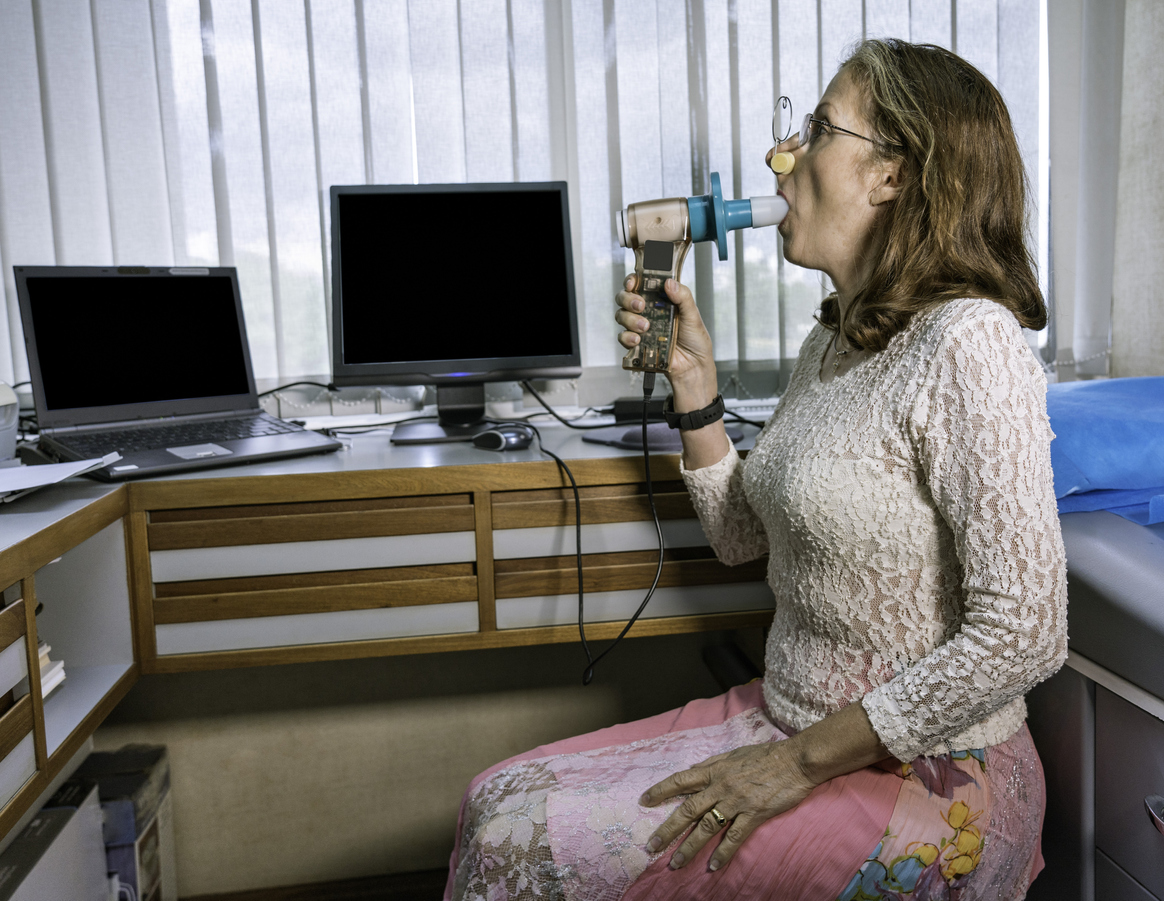

Picture source: (Link)
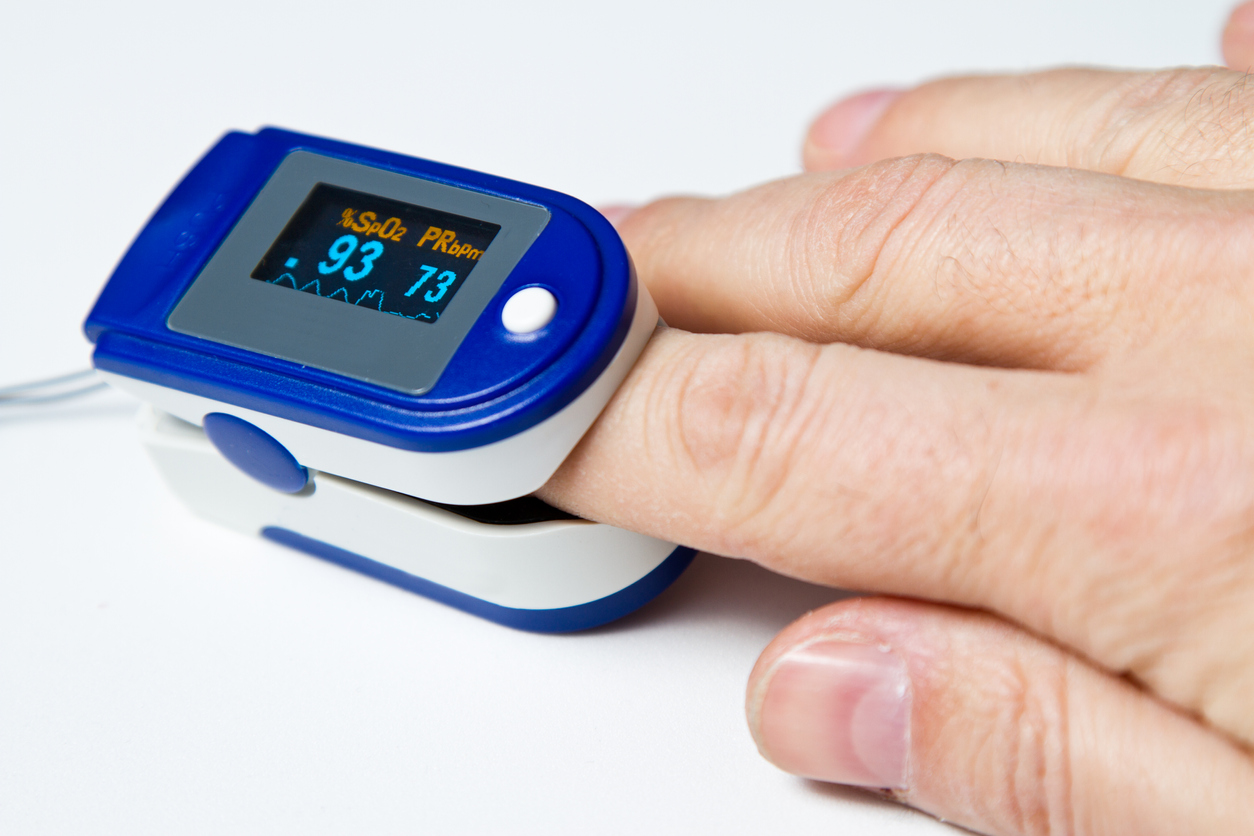
2. Finger Pulse Oximeter:
According to the UK's NHS, pulse oximetry is a noninvasive and painless test that measures oxygen saturation level. Oxygen saturation level is the amount of oxygen present in the blood. It can rapidly detect even small changes in how efficiently oxygen is being carried to the extremities furthest from the heart. The pulse oximeter is a small, clip-like device that attaches to a body part, like toes or an earlobe. It’s most commonly put on a finger and used in critical care settings like emergency rooms or hospitals. It is used to monitor the following conditions:
- Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD)
- Asthma
- Pneumonia
- Lung cancer
- Congenital heart defects
Picture source: (Link)
Lung problems like pneumonia and respiratory failure can be some of the most severe symptoms of the novel Coronavirus (the cause of COVID -19). Some individuals are prescribed a pulse oximeter for conditions that cause them to have periods of low oxygen, for certain underlying lung conditions, if someone with a lung condition is exercising or even traveling to high altitudes.
3. Bronchoscopy:
According to the NHS, a bronchoscopy is a procedure that allows a doctor to examine the inside of the lungs, including the bronchi. The bronchi are the main pathways into the lungs. During a bronchoscopy, a doctor inserts a thin tube containing a light and camera into the lungs through the nose or mouth. The doctor can use the findings to diagnose infections, tumors, or diseases in the lung.
There are two types of bronchoscopes that may be used: Flexible and rigid.
- Flexible bronchoscopy uses a long, thin, flexible lighted tube that can access the small airway branches. A sample of tissue or a biopsy may be obtained through the bronchoscope for laboratory study.
- Rigid bronchoscopy involves the use of a rigid, straight, hollow metal tube. Rigid bronchoscopy is utilized when the airway is obstructed by blood or foreign objects.
