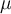Glossary - Research Basics and Terminology
This glossary explains common terminology used in research articles. It helps you to understand the articles which are included in the following chapters of this course.
If you are looking for more terminology, the glossary of 'The Cochrane Collaboration' is a useful resource which you can find here.
Special | A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | I | J | K | L | M | N | O | P | Q | R | S | T | U | V | W | X | Y | Z | ALL
H |
|---|
Hypothesis | |||
|---|---|---|---|
= statement being tested | |||
I |
|---|
Independent Variable | |||
|---|---|---|---|
Clinical trial Dependent variable = outcome (ill or healthy) Independent variable = treatment arm (new drug) | |||
Interval Scale | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| |||
L |
|---|
Levels of Evidence | |||
|---|---|---|---|
Level I: Evidence from a systematic review or meta-analysis of all relevant RCTs Level II: Evidence obtained from well-designed RCTs Level III: Evidence obtained from well-designed controlled trials without randomization Level IV: Evidence from well-designed case-control and cohort studies Level V: Evidence from systematic reviews of descriptive and qualitative studies Level VI: Evidence from single descriptive or qualitative studies Level VII: Evidence from an opinion of authorities and/ or reports of expert committees Further information: Evidence Based Practice Toolkit More information about different study types: Literature Reviews: Types of Clinical Study Designs | |||
M |
|---|
Maximum (MAX) | |||
|---|---|---|---|
Set of numbers: 3,4,5,5,5,6,7
MAX= 7 | |||
Mean (μ, x̄) | |||
|---|---|---|---|
Median | |||
|---|---|---|---|
Order all observations from smallest to highest number
Set of numbers (ordered from smallest to biggest number): 3, 4, 5, 5, 5, 6, 7
2. Even number of observations: n= 8
Set of numbers (ordered from lowest to highest number): 3, 4, 5, 5, 6, 6, 7, 9
| |||
Minimum (MIN) | |||
|---|---|---|---|
Set of numbers: 3,4,5,5,5,6,7
MIN= 3
| |||
Mode | |||
|---|---|---|---|
Set of numbers: 3, 4, 5, 5, 5, 6, 7 Mode= 5 | |||